Home>Vaccination Services> Pneumococcal Vaccination
Last update: 2025 Feb
Pneumococcal Vaccination
Pneumonia ranks as the second leading cause of death in HK surpassed only by cancer
Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae, or S. pneumoniae) is the most common bacterium causing respiratory infections in children. It can cause a wide range of infections from bronchitis, otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia, septicaemia to meningitis. The bacteria can be transmitted via spread of droplet, direct oral contact or indirect contact with articles soiled with respiratory discharges. In Hong Kong, the annual incidence of IPD ranged from 1.7 to 2.9 per 100,000. The incidence is higher in children younger than 5 years of age and adults 65 years of age and older. Pneumococcal vaccination is one of the most effective means of preventing pneumococcal diseases. Let’s learn more about vaccine information right away.
The following 4 vaccines are all approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
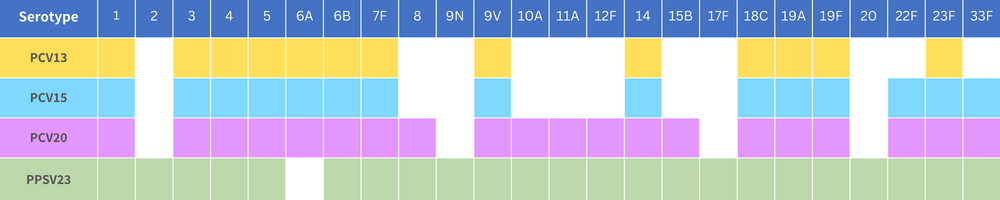
PCV13
(Prevenar 13)
- Helps protect against 13 types of pneumococcal bacteria
- At least 8 in 10 babies from serious infections called invasive pneumococcal disease
PCV15
(Vaxneuvance)
- Includes all PCV13 serotypes plus 22F and 33F
- Enhanced protection against serotype 3 pneumococcus, which is common in HK.
PCV20
(Prevnar 20)
- Currently the conjugate vaccine on the market that covers the most serotypes.
- Five more serotypes than the 15-valent vaccine.
- Number of doses
- Individuals aged 2 years old or above (including adults): only 1 injection is needed
- Individuals aged 6 weeks to 23 months : 2-4 injections
Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine
| PCV13 | PCV15 | PCV20 | PPSV23 | |
| Eligible | 6 weeks and above | 2 years and above at high risk AND65 years and above | ||
| Number of doses | 6 weeks to 7months: 3 doses 7 -11 months︰3 doses 12-23 months︰2 doses 2 years and above︰1 dose *Please consult a doctor for high-risk situations. | 6 weeks to 23 months: 4 doses 2 years and above: only 1 dose is needed | Normal︰1 dose ** High-risk situations ︰A single dose may be required again after 5 years. Please consult a doctor before vaccination. | |
| Prevention | ✓ Invasive pneumococcal disease ✓ Non-invasive pneumococcal pneumonia | ✓ Invasive pneumococcal disease ✕ Non-invasive pneumococcal pneumonia | ||
| Common side effects | Slight swelling and tenderness at the injection site shortly following injection but most resolve within two days. Some may experience mild fever, fatigue, headache, chills, or muscle pain. | Slight swelling and tenderness at the injection site shortly following injection but most resolve within two days. Fever, muscle aches or more severe local reactions are uncommon. | ||
| Covered by Vaccination Subsidy Scheme (VSS) | Infant#︰3 doses for free 65 years and above^︰1 dose with subsidy | 65 years and above^︰1 dose with subsidy | Not applicable | 65 years and above^︰1 dose with subsidy |
The above information is for reference only. Consult a medical professional for specific recommendations.
Children born in 2019 will receive two primary doses of PCV13 at two and four months, followed by a booster dose of PCV13 at 12 months at the Department of Health’s Maternal & Child Health Centres.
| Elderly without High-Risk Conditions | Elderly with High-Risk Conditions | |
| Have Not Received Any Pneumococcal Vaccine | PPSV23 x1 | PCV13/PCV15 x1 + PPSV23 x1 ﹙ one-year interval is required between doses ﹚ |
| Have Received PCV13/PCV15 | / | PPSV23 x1 ﹙ one-year interval is required between doses ﹚ |
| Have Received PPSV23 | / | PCV13/PCV15 x1 ﹙ one-year interval is required between doses ﹚ |
**Eligible individuals must provide relevant documentation for the government subsidy programme. Visit the Centre for Health Protection’s websitefor more details.
- History of invasive pneumococcal disease, cerebrospinal fluid leakage or cochlear implant
- Chronic cardiovascular (except hypertension without complication), lung, liver or kidney diseases
- Metabolic diseases including diabetes mellitus or obesity (Body Mass Index 30 or above)
- Immunocompromised states related to weakened immune system due to conditions such as asplenia, HIV/AIDS or cancer/steroid treatment
- Chronic neurological conditions that can compromise respiratory functions, the handling of respiratory secretions, increase the risk for aspiration or those who lack the ability to take care of themselves
| Vaccination Recommendations for High-Risk Children | 2-5 years old | 6-18 years old |
| Have Not Received Any Pneumococcal Vaccine | PCV13/ PCV15 | |
| Have Received PCV13/ PCV15 | Please consult with your doctor | PPSV23 |
| Vaccination Recommendations for High-Risk Adult | Above 18 years old |
| Have Not Received Any Pneumococcal Vaccine | PCV15/ PCV20 |
| Have Received PCV13 | PCV20/ PPSV23 |
| Have Received PCV15 | PPSV23 |
| Have Received PPSV23 | PCV15/ PCV20 |
| Have Received PCV13 and PPSV23 | Please consult with your doctor |
More information︰Pneumococcal Vaccination: Summary of Who and When to Vaccinatez (CDC)
Different High-Risk situations may affect the number of doses and intervals for pneumococcal vaccination. It is recommended to consult with your doctor before choosing a vaccine. Your doctor will recommend the most suitable vaccination plan based on your high-risk factors and special condition.
How severe is pneumococcal infection?
While pneumococcus is a common cause of mild illnesses such as sinus or middle ear infections, it may also cause severe or even life-threatening invasive pneumococcal diseases (IPD) such as bacteremic pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. The outcomes for IPD are usually more severe among young children and elderly persons.
Is a person previously contracted with pneumococcal disease immune from future invasive pneumococcal diseases?
As there are over 90 serotypes of pneumococcus, previous infection of a serotype of pneumococcus may not confer immunity to other serotypes of pneumococcus.
Can pneumococcal vaccines be received together with COVID-19 vaccine or seasonal influenza vaccine?
Yes. Pneumococcal vaccines can be given together with COVID-19 vaccine or seasonal influenza vaccine, but they should be administered with a different syringe and at a different injection site.
Who are not suitable to receive pneumococcal vaccines?
Severe allergic reaction following a prior dose of pneumococcal vaccine or to the vaccine component or any diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine is a contraindication to further doses of vaccine.