Cervical Pap Smear Examination
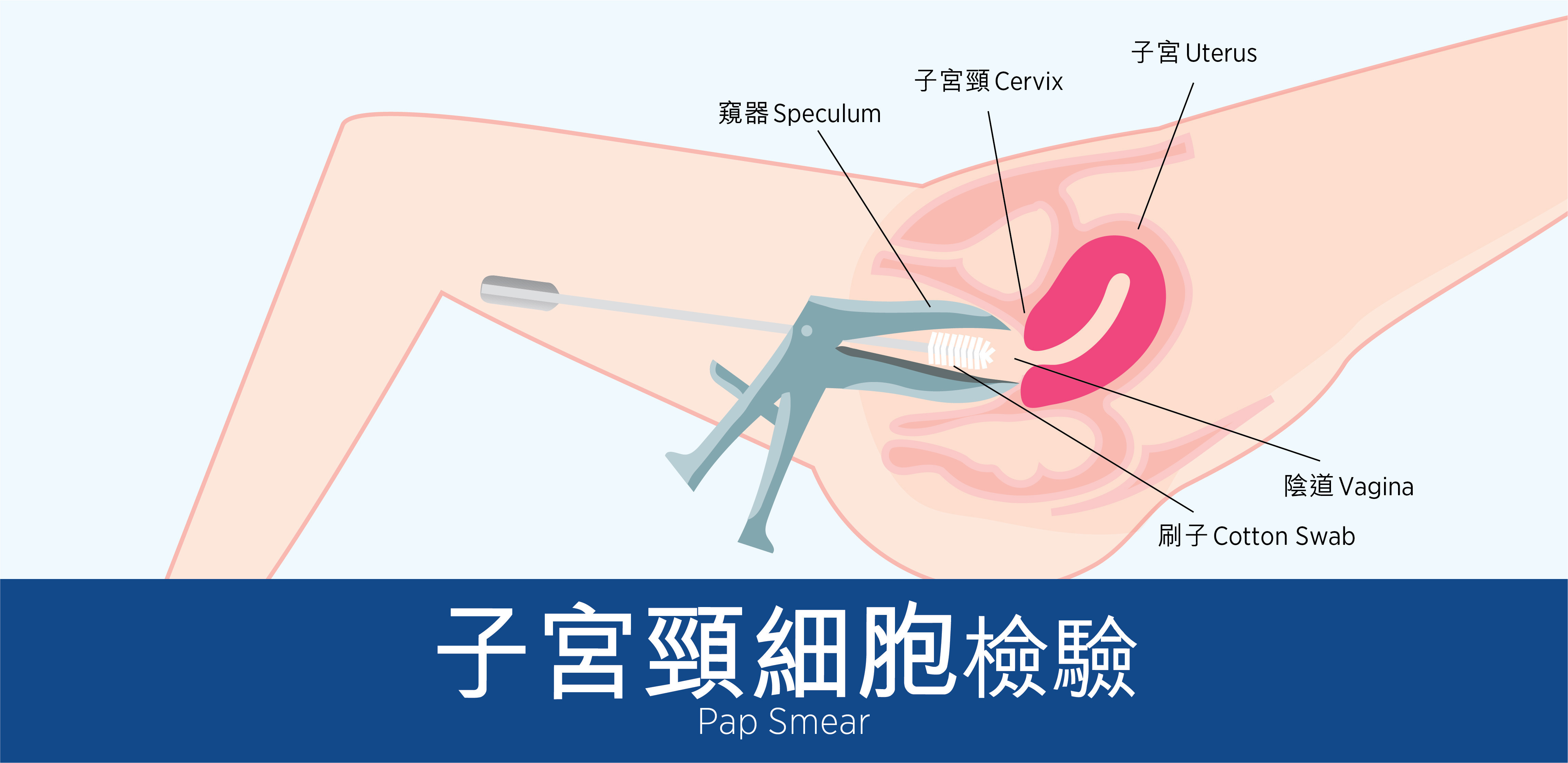
The cervical Pap smear examination is a widely used screening method for cervical cancer. It is a simple and quick procedure. The test can detect precancerous lesions or early signs of cervical cancer, making it highly effective for early detection. Generally, it is recommended that women between the ages of 25 and 64 who have been sexually active undergo regular cervical Pap smear examinations.
Content
- Cervical Pap smear examination procedure
- Do I need to undergo a cervical Pap smear examination??
- When should women undergo cervical Pap smear examinations?
- Timing and precautions for cervical Pap smear examinations
- Do women who have never had sexual experience need to undergo the examination?
- Do women who have received the HPV vaccine need to undergo the examination?
- Interpreting cervical cell test results
Cervical Pap smear examination procedure
During a cervical Pap smear examination, the doctor will gently collect cell samples from the surface of the cervix using a brush or spatula. These samples are then sent to the laboratory for analysis. Here are the steps involved in a cervical Pap smear examination:
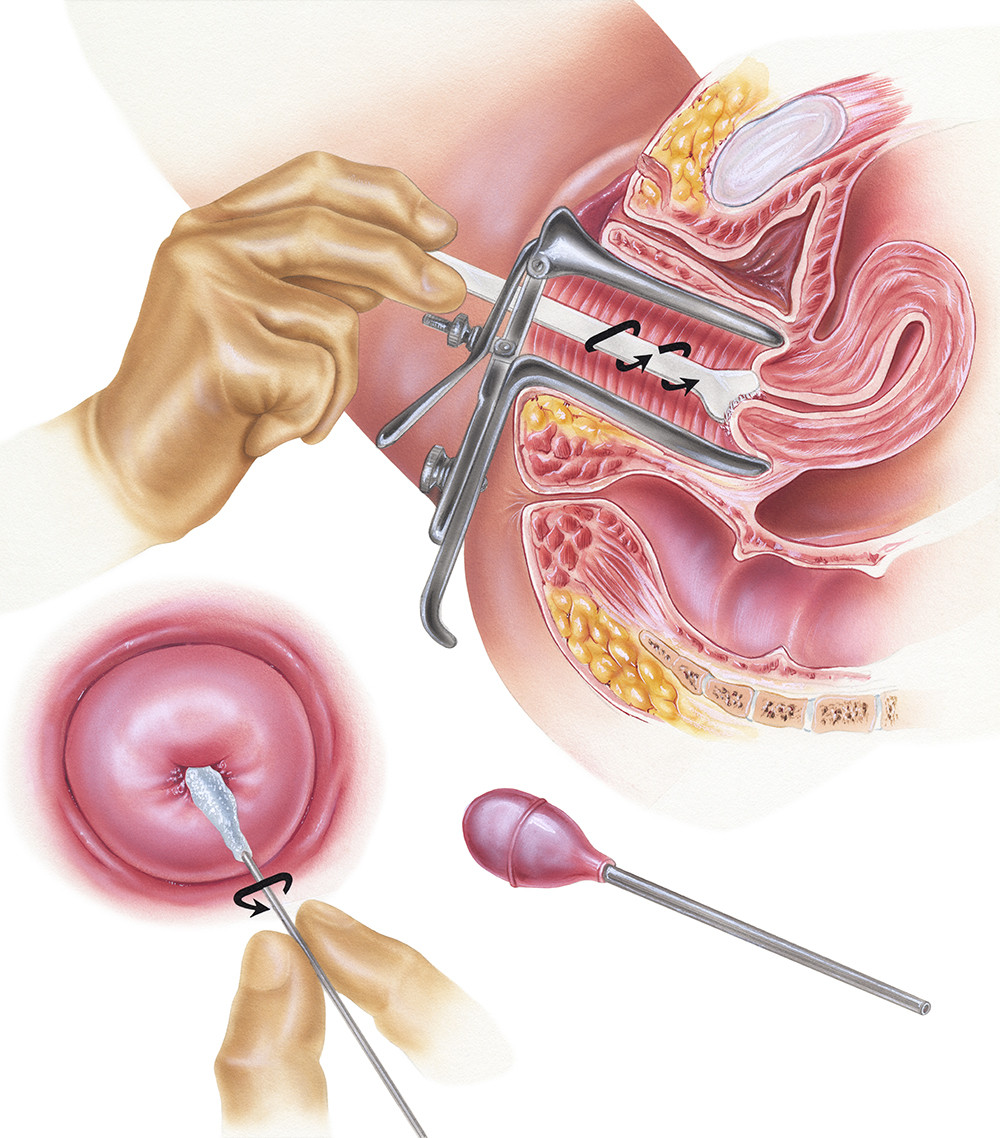
- The patient lies down on the examination table with their legs apart and supported.
- The doctor uses a speculum to gently open the vaginal walls, allowing access to the cervix.
- Using a brush or spatula, the doctor gently scrapes the surface of the cervix to collect cell samples. This process may cause slight discomfort, but it generally does not result in severe pain.
- The collected cell samples are placed on a glass slide or stored in a liquid preservative and then sent to the laboratory for analysis.
- In the laboratory, trained professionals examine the cell samples under a microscope to evaluate the appearance and structure of the cells. They will determine if the cells are normal and may also investigate the presence of abnormal cell changes, such as cellular dysplasia (abnormal changes in cell morphology) or precancerous lesions.
Do I need to undergo a cervical Pap smear examination?
Cervical Pap smear examinations are recommended for women without symptoms as part of cervical cancer screening. In general, women between the ages of 25 and 64 who have had sexual experience should undergo regular cervical Pap smear examinations.
- Women aged 65 or above who have had three consecutive normal cervical cell test results within the past 10 years may discontinue the examination.
- Women aged 65 or above who have had sexual experience but have never undergone a cervical Pap smear examination should still undergo the examination, regardless of whether they have reached menopause, have abstained from sexual activity for many years, or have undergone sterilization surgery.
- For women between the ages of 21 and 24 who have had sexual experience, it is advisable to consult a doctor and assess the need for an examination if they have risk factors for cervical cancer, such as having multiple sexual partners.
When should women undergo cervical Pap smear examinations?
Women who have had sexual experience should begin receiving regular cervical Pap smear examinations at the age of 25.
- If the results of the first cervical cell test are normal, the next examination can be scheduled for one year later.
- If the results of the second examination are also normal, subsequent examinations can be conducted every three years.
- If any symptoms, such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, occur, it is important to seek medical attention promptly, even if the most recent examination results were normal.
Timing and precautions for cervical Pap smear examinations
- It is recommended to schedule a cervical Pap smear examination between the 10th and 20th day after the completion of the menstrual period. During this time, there is typically less cervical secretion, which can contribute to obtaining more accurate results. It is important to avoid undergoing the examination during the menstrual period or if there is any vaginal bleeding.
- Refrain from having vaginal intercourse within 48 hours before the examination.
- Avoid using douches, vaginal suppositories, lubricants, spermicides, or any other vaginal preparations within 48 hours before the examination to prevent potential interference with the accuracy of the examination results.
Do women who have never had sexual experience need to undergo the examination?
Women who have never engaged in sexual activity do not need to undergo cervical Pap smear examinations.
Do women who have received the HPV vaccine need to undergo the examination?
Even if you have received the HPV vaccine, it is still necessary to undergo regular cervical Pap smear examinations. The HPV vaccine does not provide complete protection against all types of HPV infections, nor does it eliminate the virus if you are already infected. Therefore, routine screenings are essential for early detection and prevention of cervical abnormalities or cancer.
Interpreting cervical cell test results
Test Result: Negative
A negative result indicates that no abnormal cells were detected in the cervix. However, it is still important to continue with regular screenings as advised above.
Test Result: Positive/Abnormal
A positive or abnormal result indicates changes in cervical cells, but it does not necessarily mean cancer. Most abnormal cells are caused by HPV infection. A small percentage of women may have precancerous changes and require treatment to prevent the development of cancer. It is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo further testing.
It is important to remember that cervical Pap smear examinations, while effective in screening for cervical cancer, are not 100% accurate. It is still crucial to remain vigilant about your health and seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
Our Team
Virtus Obstetrics and Gynaecology Specialist
More:
-
Specialty Service - Obstetrics and Gynaecology
-
Health Check - Mammography